Knowledge Base
Generative AI Overview

Generative AI is a type of artificial intelligence designed to create new content, rather than just analyze or process existing data. Unlike traditional AI, which might classify data, predict trends, or detect anomalies, generative AI can produce text, images, audio, video, code, and even 3D models that resemble human-created work. It “learns” patterns from large datasets and uses them to generate outputs that are original, coherent, and contextually relevant.
Generative AI models, like large language models (LLMs) or generative adversarial networks (GANs), are trained on massive datasets. They learn statistical patterns, relationships, and structures within the data so they can produce new content that aligns with what they’ve learned.
- Text generation: Chatbots, automated reports, marketing copy, or creative writing.
- Image and video creation: AI-generated art, realistic deepfakes, or product design mockups.
- Code generation: Tools like GitHub Copilot help developers write software faster.
- Data augmentation: Creating synthetic data for training other AI systems.
From an Enterprise Perspective - Generative AI is a powerful tool for automation, creativity, and efficiency, particularly when integrated into workflows, marketing, software development, and knowledge management systems.
How Does Generative AI Work?
Generative AI is a type of artificial intelligence that creates new content — text, images, audio, video, code, and more — by learning patterns from large amounts of existing data. Here’s a clear, step-by-step explanation of how it works.
1. Training: Learning Patterns from Data
- Generative AI systems are trained on massive datasets (books, websites, images, audio, etc.).
- During training, the model:
- Looks at millions or billions of examples
- Learns patterns, structures, and relationships
- Adjusts internal parameters (often billions of them)
- Improves its predictions over time
- This does not mean that Generative AI memorize everything; it learns statistical relationships like:
- Which words tend to follow other words
- What shapes and textures form a cat
- What melodies sound harmonious
- What code structures are common in Python
- At its core, it learns: "Given this input, what is most likely to come next?”
2. Neural Networks: The Engine
- Most modern generative AI uses deep neural networks.
- These are layered mathematical systems that:
- Take input (text, image pixels, etc.)
- Transform it through many layers
- Output a prediction
- For text systems like ChatGPT, the key architecture is called a: Transformer
- Transformers are especially good at understanding context — meaning they don’t just look at the last word, but at the entire sentence or conversation.
- Example: “The bank was near the river.”
- The model understands "bank" means riverbank, not financial bank — because it processes context.
3. The Core Task: Prediction
- For text models, training is usually based on:
- Next-word prediction
- Example Input: "The sky is...."
- The model calculates probabilities:
- blue (72%)
- cloudy (12%)
- falling (0.0001%)
- green (0.3%)
- The AI model picks one based on probability rules. By predicting billions of next words during training, it becomes good at generating coherent text.
4. Generation: Creating New Content
- When you prompt a model: "Write a poem about space."
- The system:
- Converts your words into numerical representations
- Predicts the next word
- Adds it to the sentence
- Repeats this process rapidly
- Produces full text one token at a time
- It’s essentially doing very advanced predictive completion.
Other Types of Generative AI
Generative AI isn't just text, it can also create images, videos, sounds, musics, etc.; often uses:
- Diffusion models: A diffusion model is a type of generative AI model that creates data (like images, audio, or text embeddings) by learning how to gradually remove 'noise' from random input.
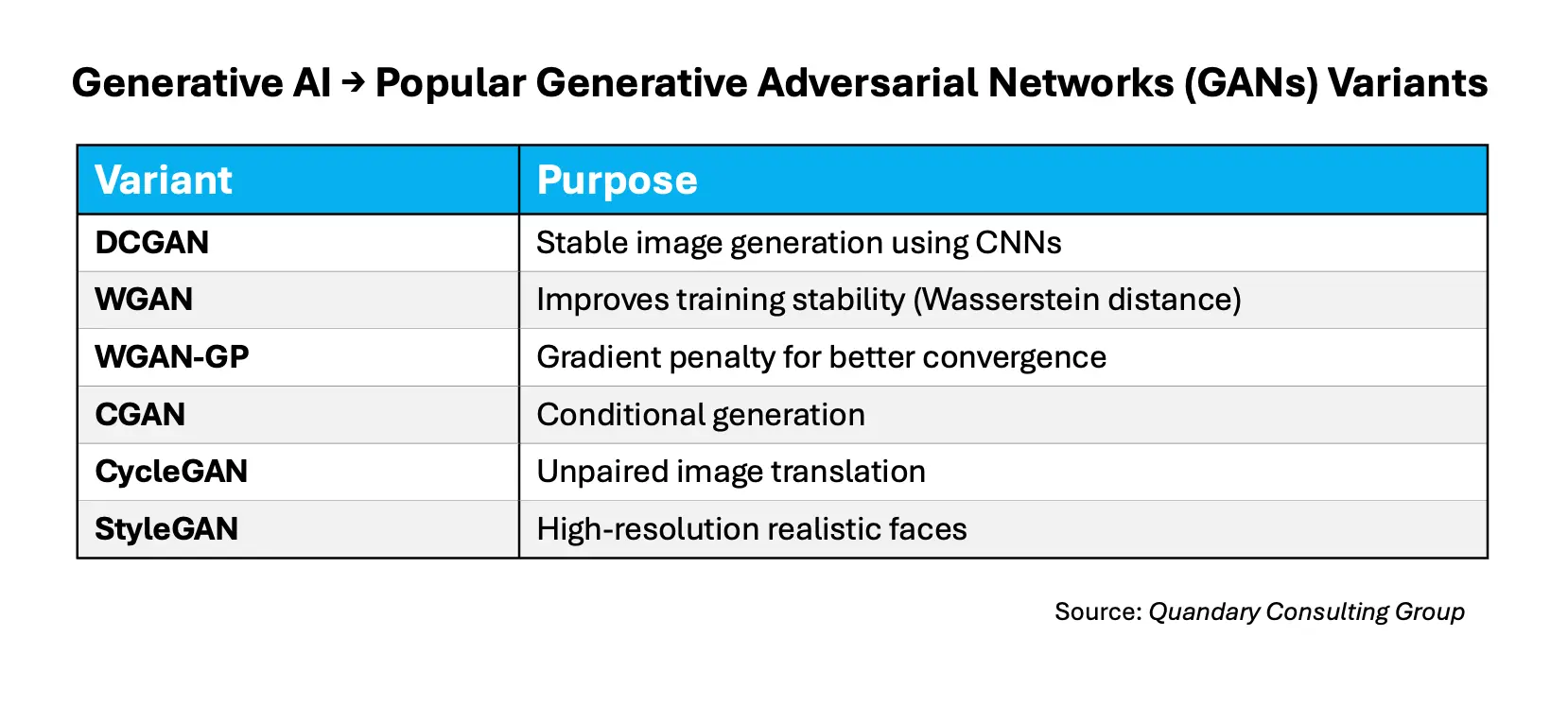
- GANs (Generative Adversarial Networks): Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) are a type of deep learning model used to generate new data that looks like real data. They can learn complex data distributions without being explicitly programmed, making them one of the most important advances in generative AI.
- GANs revolutionized generative modeling by:
- Producing extremely realistic images (eg., deep fakes)
- Advancing creative AI
- Enabling synthetic data generation
- GANs revolutionized generative modeling by:
Benefits & Risks of Generative AI
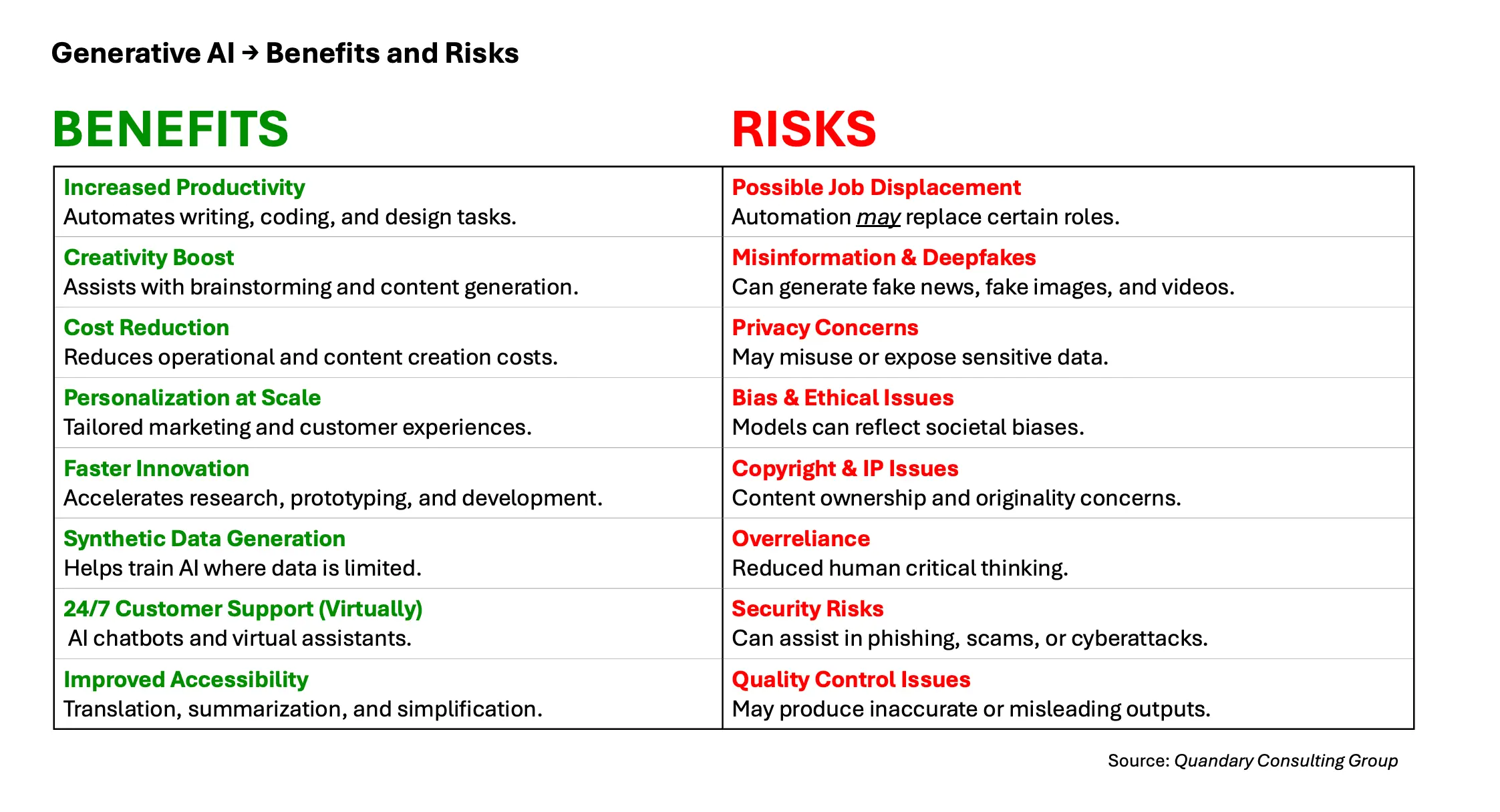
Generative AI is rapidly transforming how organizations create content, automate processes, and innovate at scale. By enabling systems to generate text, images, code, and other digital assets, it offers significant benefits such as increased productivity, cost efficiency, enhanced creativity, and personalized user experiences.
However, alongside these advantages come important risks, including data privacy concerns, misinformation, bias, intellectual property challenges, and potential job displacement. Understanding both the opportunities and the limitations of generative AI is essential for responsible adoption, effective governance, and long-term value creation.
Gen AI Real World Use Cases
Generative AI ('Gen AI') and its ability to 'create' new data has proven to be useful across all industries. There are hundreds of use cases that Generative AI can be applied to - Here are our top 10 Gen AI real world use cases that we have seen provide immediate ROI to some of our clients:
Content Creation & Copywriting
- Description: Automatically generate articles, marketing copy, social media posts, product descriptions, and blogs.
- Enterprise benefit: Saves time, ensures consistency, and scales content marketing.
- Example: AI writes personalized email campaigns for different customer segments.
Code Generation & Software Development
- Description: Generate code snippets, auto-complete functions, or even full software modules.
- Enterprise benefit: Accelerates development cycles and reduces human error.
- Example: GitHub Copilot suggests code while developers write.
Chatbots & Conversational AI
- Description: Power customer support, internal help desks, or virtual assistants with human-like responses.
- Enterprise benefit: Reduces support costs, increases response speed, and improves user experience.
- Example: A bank uses AI to answer routine customer inquiries 24/7.
Image & Video Generation
- Description: Create realistic images, graphics, animations, or video content from text prompts.
- Enterprise benefit: Cuts design costs, accelerates creative projects, and allows rapid prototyping.
- Example: Fashion companies generate virtual product visuals for e-commerce without photography.
Data Augmentation & Synthetic Data
- Description: Produce synthetic datasets to train other AI models where real data is scarce or sensitive.
- Enterprise benefit: Improves AI model performance, ensures privacy, and reduces data collection costs.
- Example: Self-driving car companies generate synthetic road scenarios for training.
Personalized Recommendations
- Description: Generate tailored suggestions for products, services, or content based on user behavior.
- Enterprise benefit: Increases engagement, conversion rates, and customer loyalty.
- Example: Streaming platforms suggest new movies with AI-generated summaries or visuals.
Knowledge Management & Document Summarization
- Description: Summarize, rewrite, or extract insights from large volumes of text or documents.
- Enterprise benefit: Improves decision-making, speeds research, and enhances productivity.
- Example: AI digests legal contracts and highlights key clauses automatically.
Design & Product Prototyping
- Description: Generate design concepts for architecture, industrial products, or digital interfaces.
- Enterprise benefit: Speeds ideation cycles and reduces cost of physical prototypes.
- Example: Automotive designers generate new car models with AI-assisted CAD tools.
Marketing & Advertising Optimization
- Description: Generate ad copy, visuals, and campaigns tailored to audience segments.
- Enterprise benefit: Enhances engagement, boosts ROI, and allows rapid A/B testing.
- Example: AI creates multiple ad variations and tests them for effectiveness automatically.
Scientific Research & Drug Discovery
- Description: Generate chemical compounds, simulate experiments, or suggest hypotheses.
- Enterprise benefit: Accelerates R&D cycles and reduces trial-and-error costs.
- Example: Pharma companies use AI to propose molecules for new drugs or vaccines.
The Importance of Generative AI
Generative AI is important because it fundamentally changes how humans create, solve problems, and scale knowledge work. Unlike traditional software that follows fixed rules, generative AI can learn patterns from large amounts of data and produce new content—such as text, images, code, audio, and designs—on demand.
This ability dramatically increases productivity, accelerates innovation, and lowers barriers to creativity and technical expertise. It enables businesses to personalize services at scale, automate complex tasks, and prototype ideas faster than ever before.
At the same time, it reshapes industries by transforming how content is produced, how software is developed, and how people interact with technology, making it one of the most impactful technological advancements of the modern digital era.
In Conclusion
Generative AI represents a transformative force for modern enterprises. It is not just a tool for automation or creativity—it is a strategic lever that can accelerate innovation, streamline operations, and unlock entirely new business models.
From content generation and product design to data augmentation and knowledge management, these technologies enable organizations to work faster, smarter, and with greater precision. However, realizing the full potential of generative AI requires intentional strategy, robust governance, and thoughtful integration into enterprise workflows.
Leaders must consider ethical implications, data privacy, and alignment with long-term business objectives, ensuring that AI-generated outputs enhance decision-making rather than introduce risk.
In addition, by embedding AI capabilities into processes, systems, customer experiences, etc., companies can achieve measurable efficiency gains, improved innovation pipelines, and a competitive edge in increasingly dynamic markets.
The opportunity is very clear: Adopt generative AI not as a novelty, but as a strategic asset, one that scales human ingenuity, informs critical decisions, and accelerates enterprise transformation. Quandary Consulting Group is dedicating to helping leaders navigate this journey, ensuring AI initiatives deliver tangible business outcomes while maintaining operational resilience and governance rigor.
- By: Kevin Shuler
- Email: kevin@quandarycg.com
- Date: 02/08/2026
Resources
© 2026 Quandary Consulting Group. All Rights Reserved.
Privacy Policy


